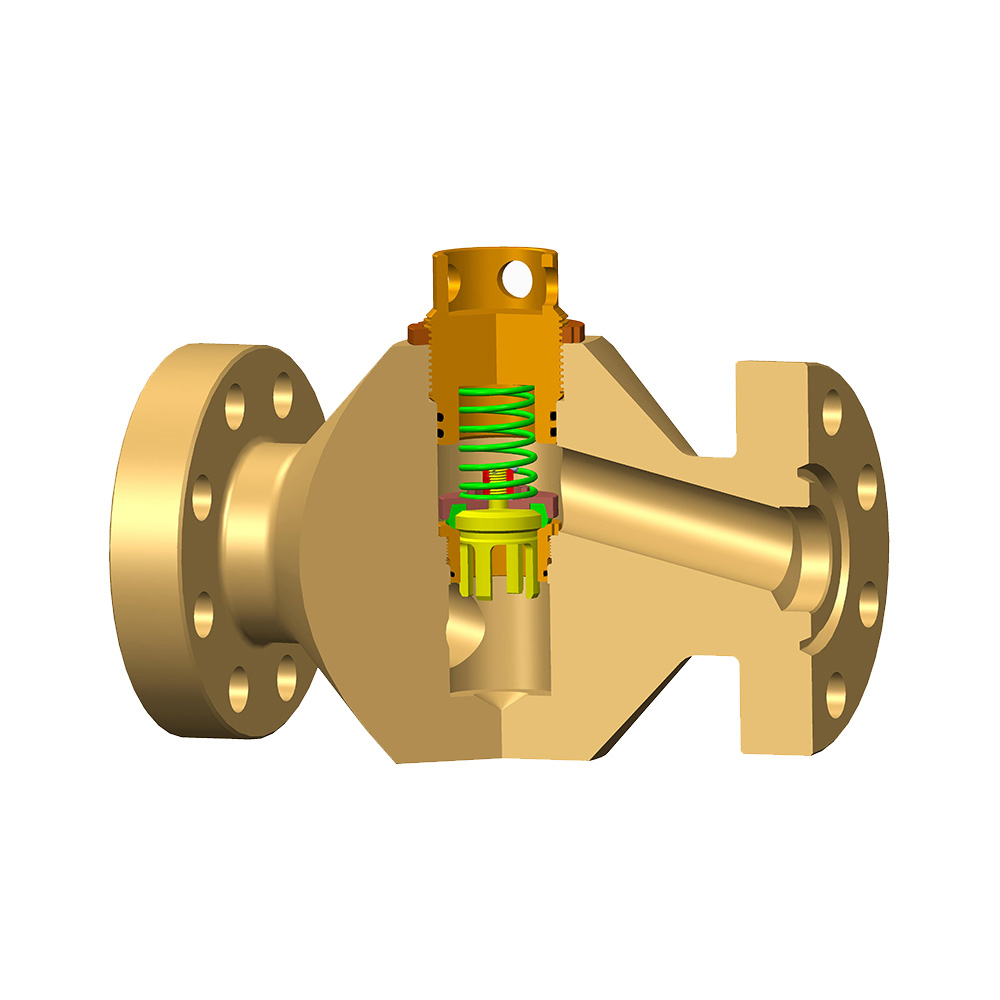
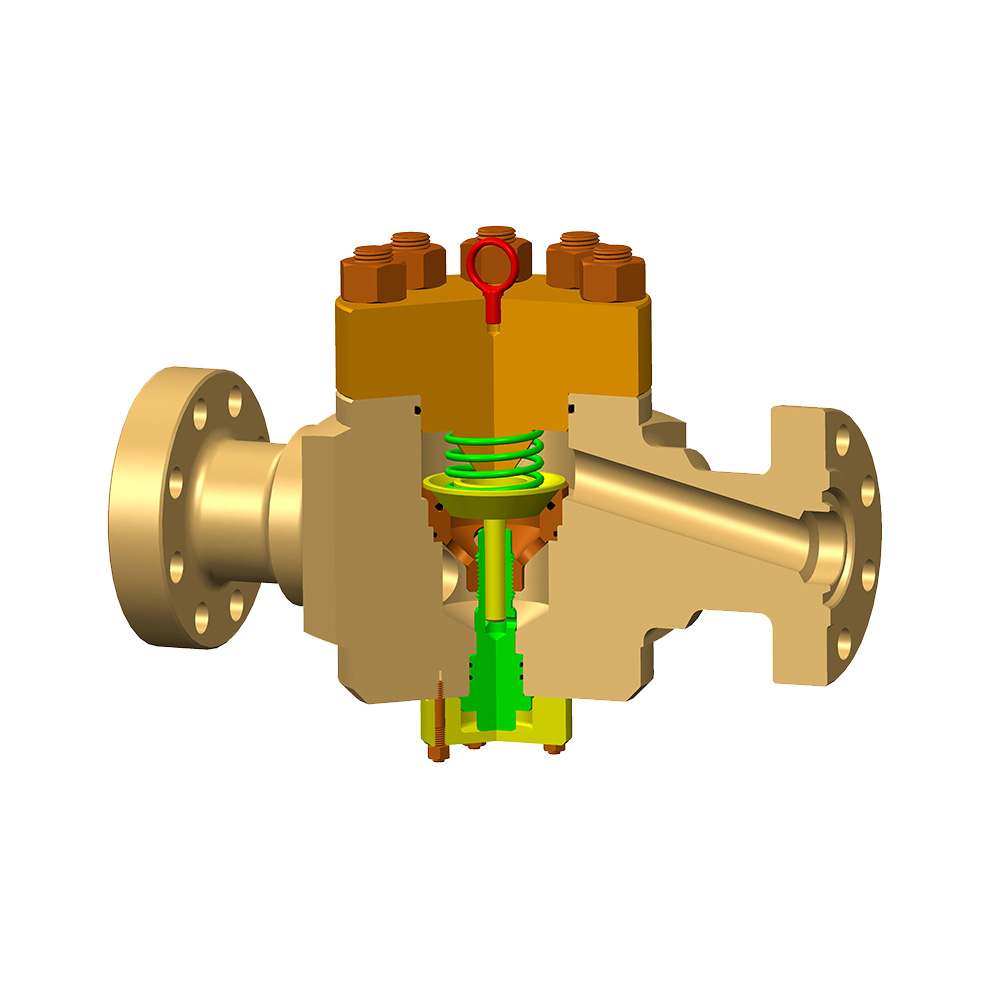
An Expanding Gate Valve is a critical flow control device widely used in oil and gas, petrochemical, pipeline transportation, and other industrial systems where tight shut-off, bidirectional sealing, and high reliability are required. Its unique expanding mechanism differentiates it from conventional gate valves, allowing superior sealing performance under varying pressure conditions.
To fully understand how an Expanding Gate Valve works and why it performs so effectively, it is essential to examine its main components in detail. Each component plays a specific role in ensuring sealing integrity, durability, and operational efficiency.
- Main Components of an Expanding Gate Valve
- How the Expanding Gate Valve Works
- Comparison: Expanding Gate Valve vs Other Gate Valves
- Key Advantages of an Expanding Gate Valve
- Typical Applications
- Maintenance Considerations
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What makes an Expanding Gate Valve different from a standard gate valve?
- Is an Expanding Gate Valve suitable for low-pressure systems?
- Can an Expanding Gate Valve be used for bidirectional flow?
- Does the expanding mechanism increase maintenance requirements?
- Which industries benefit most from Expanding Gate Valves?
- Conclusion
Main Components of an Expanding Gate Valve
Valve Body
The valve body is the primary pressure-containing component of an Expanding Gate Valve. It houses all internal parts and connects the valve to the pipeline system.
- Typically manufactured from carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, or forged steel
- Designed to withstand high pressure, temperature, and corrosive media
- Available in flanged, welded, or threaded end connections
The internal cavity of the valve body is precisely machined to support the expanding gate mechanism and ensure smooth operation. A robust body design minimizes deformation under pressure, directly contributing to reliable sealing.
Valve Bonnet
The valve bonnet forms the upper enclosure of the Expanding Gate Valve and provides a sealed chamber for the stem and gate movement.
- Bolted or pressure-sealed bonnet designs depending on pressure class
- Provides structural support for the stem
- Allows maintenance access to internal components
High-quality bonnet sealing is essential to prevent external leakage, especially in hazardous fluid applications.
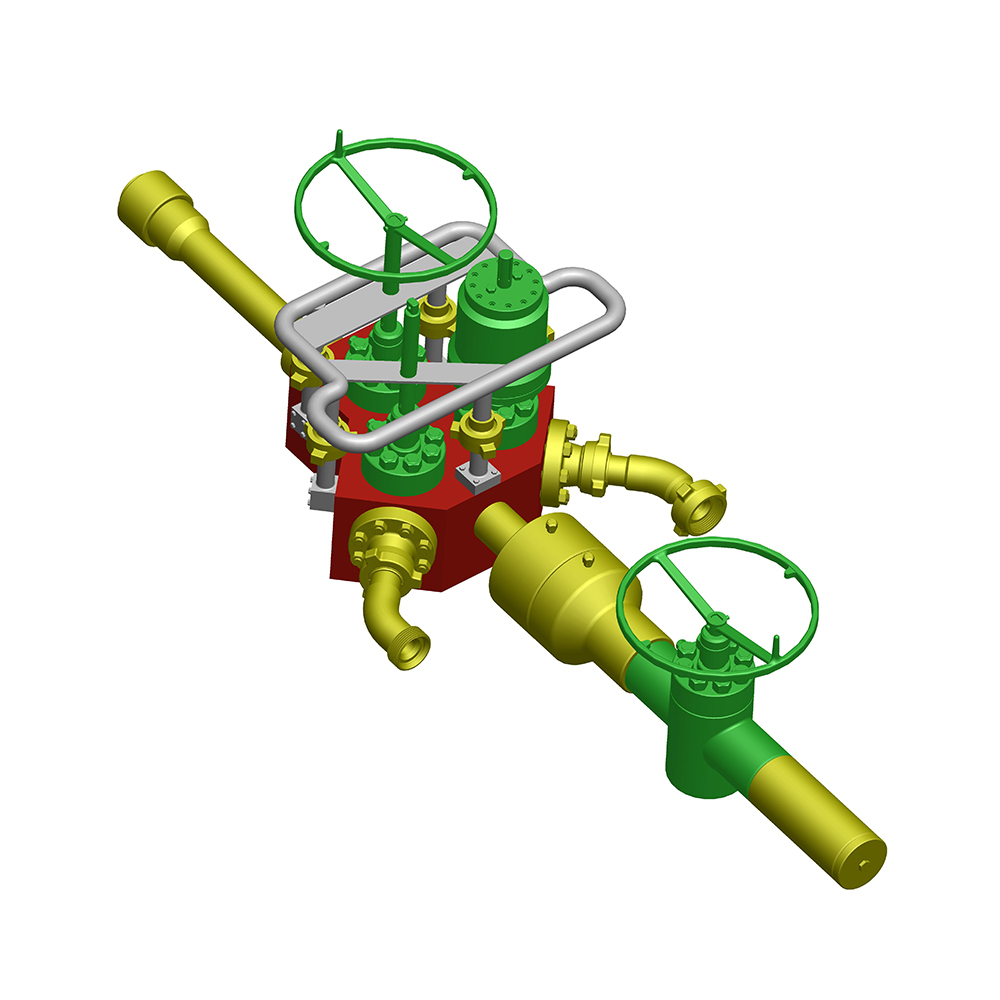
Expanding Gate Assembly
The expanding gate assembly is the defining feature of an Expanding Gate Valve. Unlike a single-piece gate, this assembly consists of multiple components that expand against the valve seats to achieve a tight seal.
Gate Segments
Most Expanding Gate Valves use a two-piece gate design:
- Two independent gate segments
- Precision-machined sealing surfaces
- Capable of expanding outward under mechanical force
When the valve closes, the gate segments move apart, pressing firmly against the valve seats and creating a positive mechanical seal.
Wedge or Spreader
The wedge or spreader sits between the gate segments and forces them outward during valve closure.
- Ensures uniform contact with both seats
- Compensates for seat wear over time
- Improves sealing performance at low and high pressure
This mechanical expansion eliminates dependence on line pressure, a key advantage of the Expanding Gate Valve design.
Valve Seats
The valve seats provide the sealing interface between the gate assembly and the valve body.
- Fixed or floating seat designs
- Metal-to-metal or metal-to-soft sealing options
- Hardened surfaces for wear resistance
High-quality seat materials and precise alignment are crucial for achieving zero leakage in critical service conditions.
Stem
The valve stem transmits motion from the actuator or handwheel to the expanding gate assembly.
- Rising stem or non-rising stem configurations
- Manufactured from corrosion-resistant alloys
- Designed to handle high torque loads
A smooth and accurately machined stem ensures reliable gate movement and long service life.
Stem Nut and Yoke
The stem nut converts rotary motion into linear movement, while the yoke supports the stem and actuator.
- Stem nut often made from bronze or special alloys
- Yoke provides structural stability
- Ensures precise alignment of stem movement
Actuation System
An Expanding Gate Valve can be operated using different actuation methods depending on application requirements.
- Manual handwheel or gear operator
- Pneumatic actuator
- Electric actuator
- Hydraulic actuator
Automated actuation is common in remote pipeline and process control systems.
Sealing Elements and Packing
Sealing elements prevent leakage around the stem and body joints.
- Stem packing made from graphite or PTFE
- Body-bonnet gaskets for pressure containment
- Designed for easy adjustment and replacement
How the Expanding Gate Valve Works
When the valve is closed, the stem drives the gate assembly downward. As the gate reaches the closed position, the wedge forces the two gate segments outward against the valve seats. This mechanical expansion creates a tight seal on both sides of the valve, independent of pipeline pressure.
During opening, the wedge disengages, allowing the gate segments to retract and move freely without dragging against the seats, reducing wear.
Comparison: Expanding Gate Valve vs Other Gate Valves
Expanding Gate Valve vs Solid Wedge Gate Valve
- Sealing Performance: Expanding Gate Valve provides superior sealing at low pressure
- Wear Compensation: Expanding design compensates for seat wear
- Complexity: Expanding Gate Valve has more components
Expanding Gate Valve vs Parallel Slide Gate Valve
- Sealing Method: Mechanical expansion vs pressure-assisted sealing
- Bidirectional Sealing: Expanding Gate Valve excels in both directions
- Maintenance: Parallel slide valves may require more frequent seat attention
Expanding Gate Valve vs Ball Valve
- Flow Path: Full-bore flow in both designs
- Shut-off Reliability: Expanding Gate Valve preferred for critical isolation
- Operating Speed: Ball valves operate faster
Key Advantages of an Expanding Gate Valve
- Excellent sealing performance regardless of pressure
- True bidirectional shut-off capability
- Reduced seat wear during operation
- Long service life in demanding applications
- Suitable for pigging operations in pipelines
Typical Applications
- Oil and gas transmission pipelines
- Refining and petrochemical facilities
- Natural gas storage and distribution
- High-pressure isolation systems
Maintenance Considerations
Proper maintenance ensures optimal performance of an Expanding Gate Valve:
- Regular inspection of stem packing
- Periodic lubrication of stem and nut
- Monitoring seat and gate wear
- Ensuring actuator alignment
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What makes an Expanding Gate Valve different from a standard gate valve?
An Expanding Gate Valve uses a mechanical expansion mechanism that forces the gate against the seats, providing reliable sealing independent of line pressure.
Is an Expanding Gate Valve suitable for low-pressure systems?
Yes, the mechanical sealing design allows excellent performance even in low-pressure or no-pressure conditions.
Can an Expanding Gate Valve be used for bidirectional flow?
Yes, it offers true bidirectional sealing, making it ideal for pipeline isolation.
Does the expanding mechanism increase maintenance requirements?
While the internal structure is more complex, proper design and materials result in long service intervals and reduced seat wear.
Which industries benefit most from Expanding Gate Valves?
Oil and gas, petrochemical, pipeline transportation, and high-integrity isolation systems benefit the most from Expanding Gate Valve technology.
Conclusion
The Expanding Gate Valve stands out as a highly reliable and efficient isolation solution due to its unique expanding gate mechanism and robust component design. Understanding its main components—from the valve body and bonnet to the expanding gate assembly and sealing elements—helps engineers and operators select, operate, and maintain these valves with confidence in demanding industrial environments.