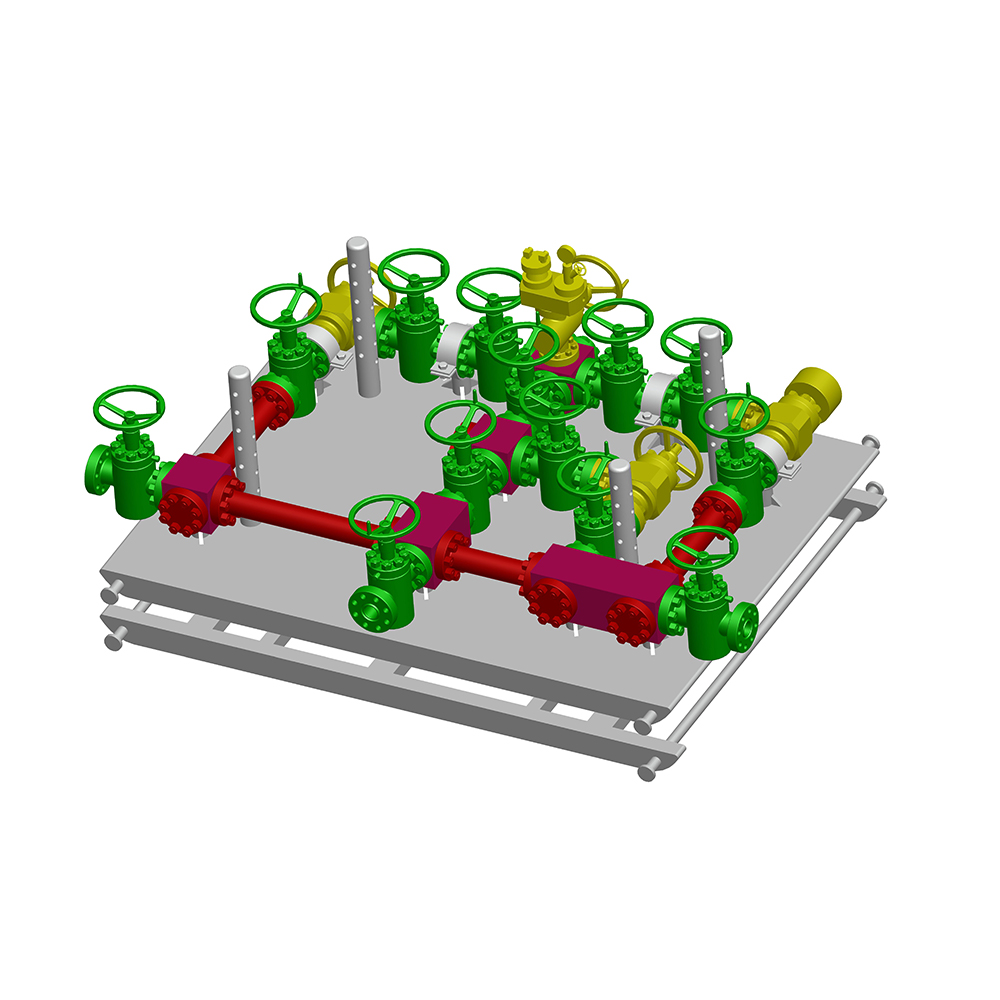
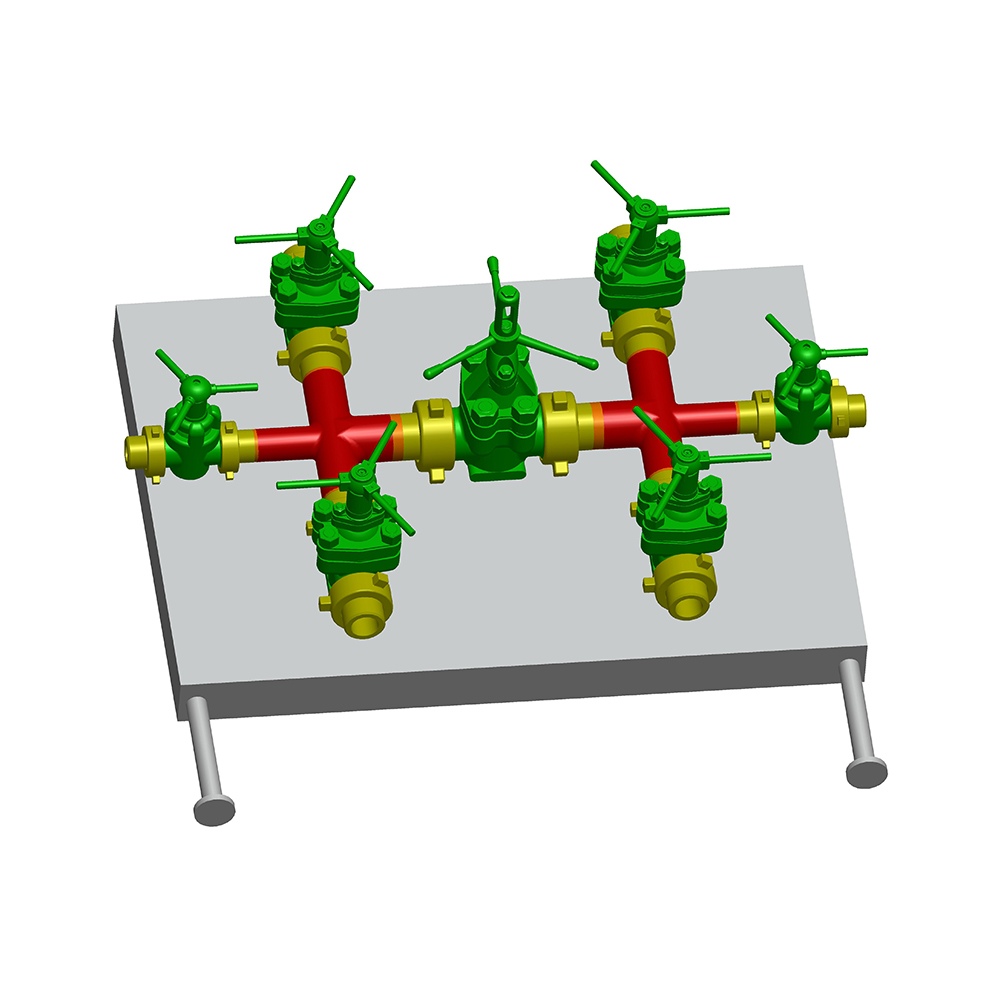
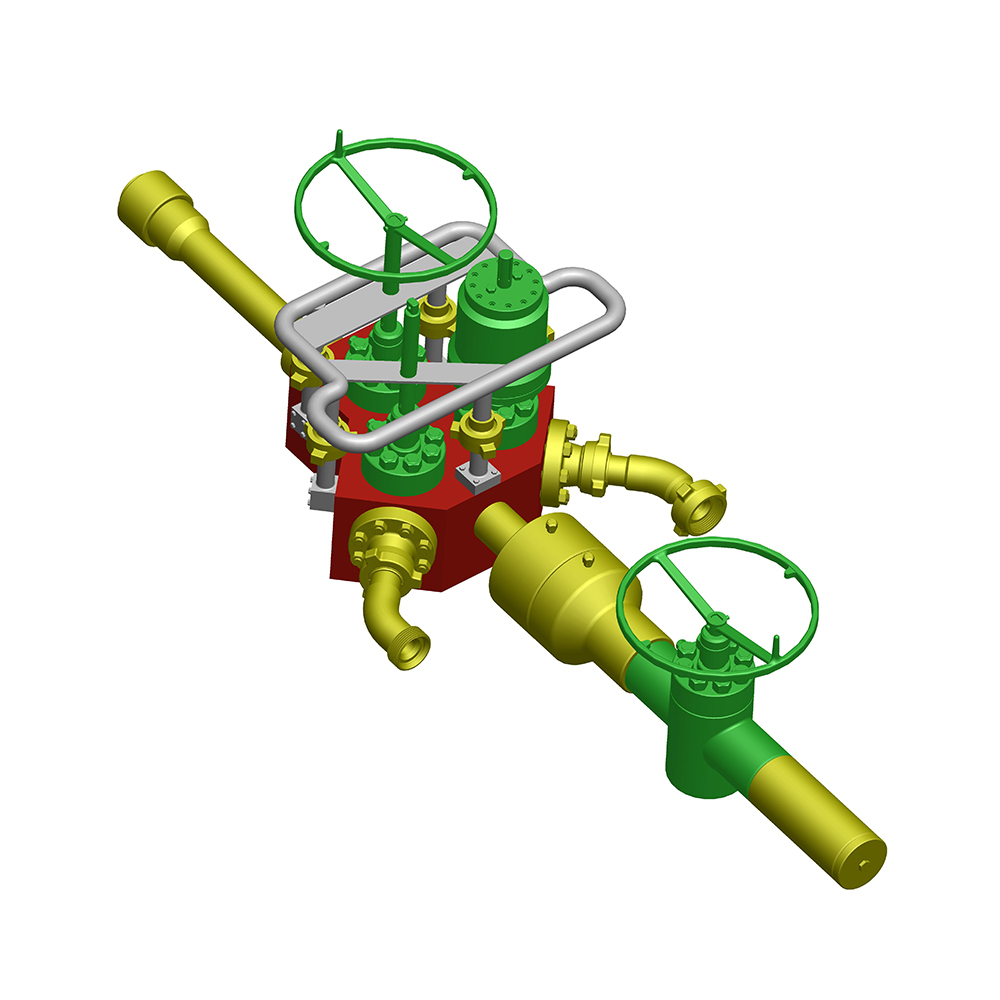
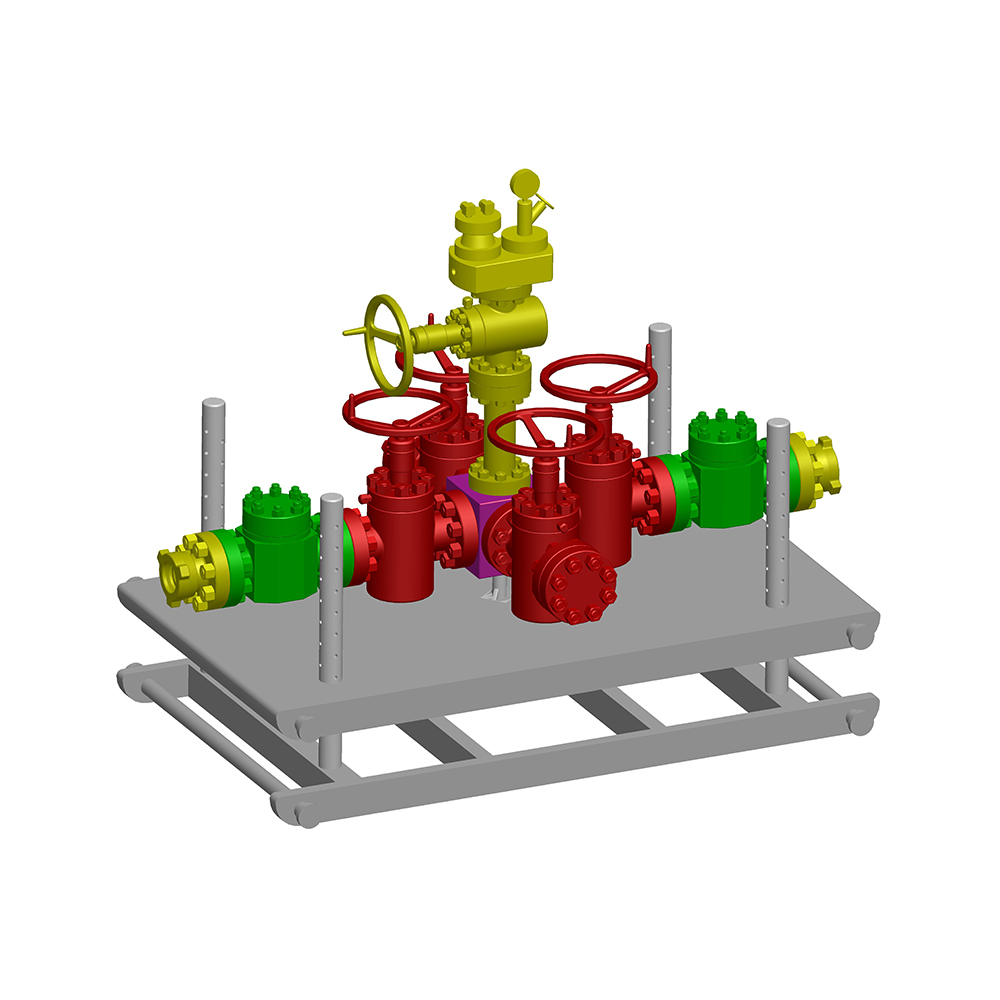
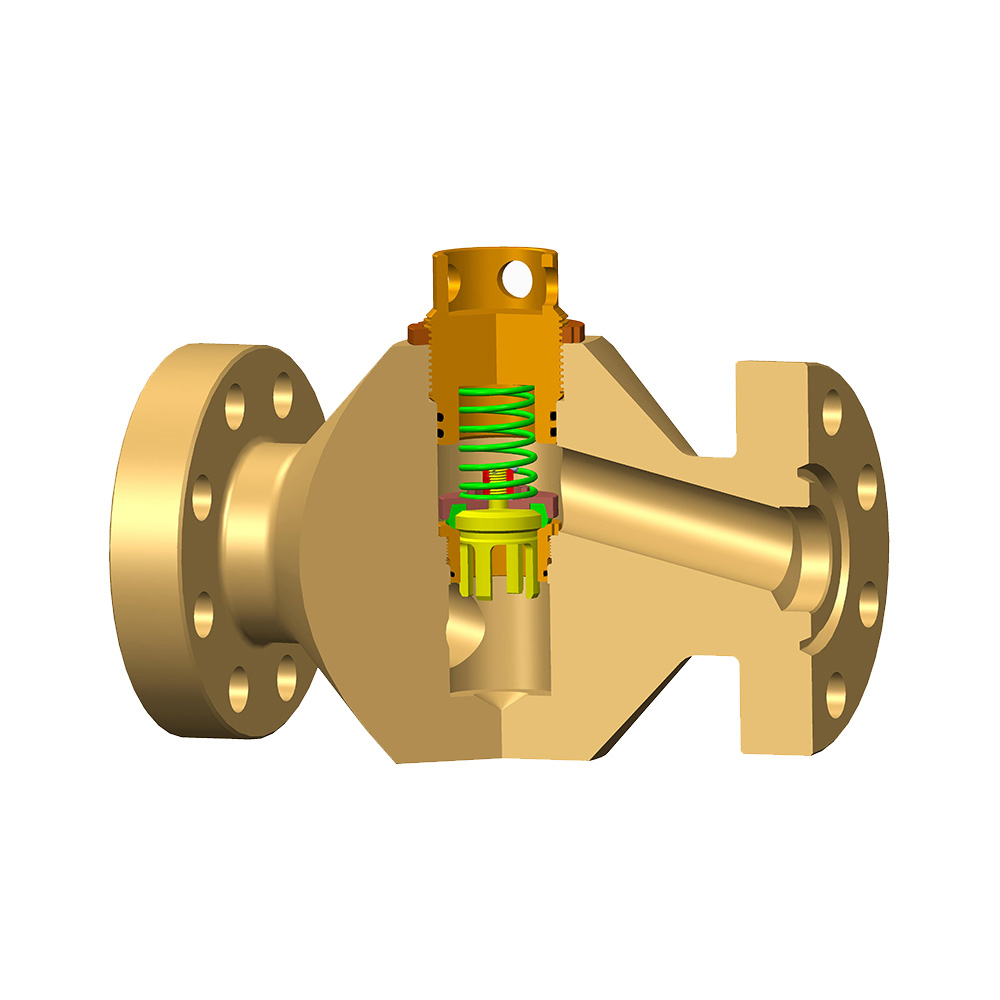
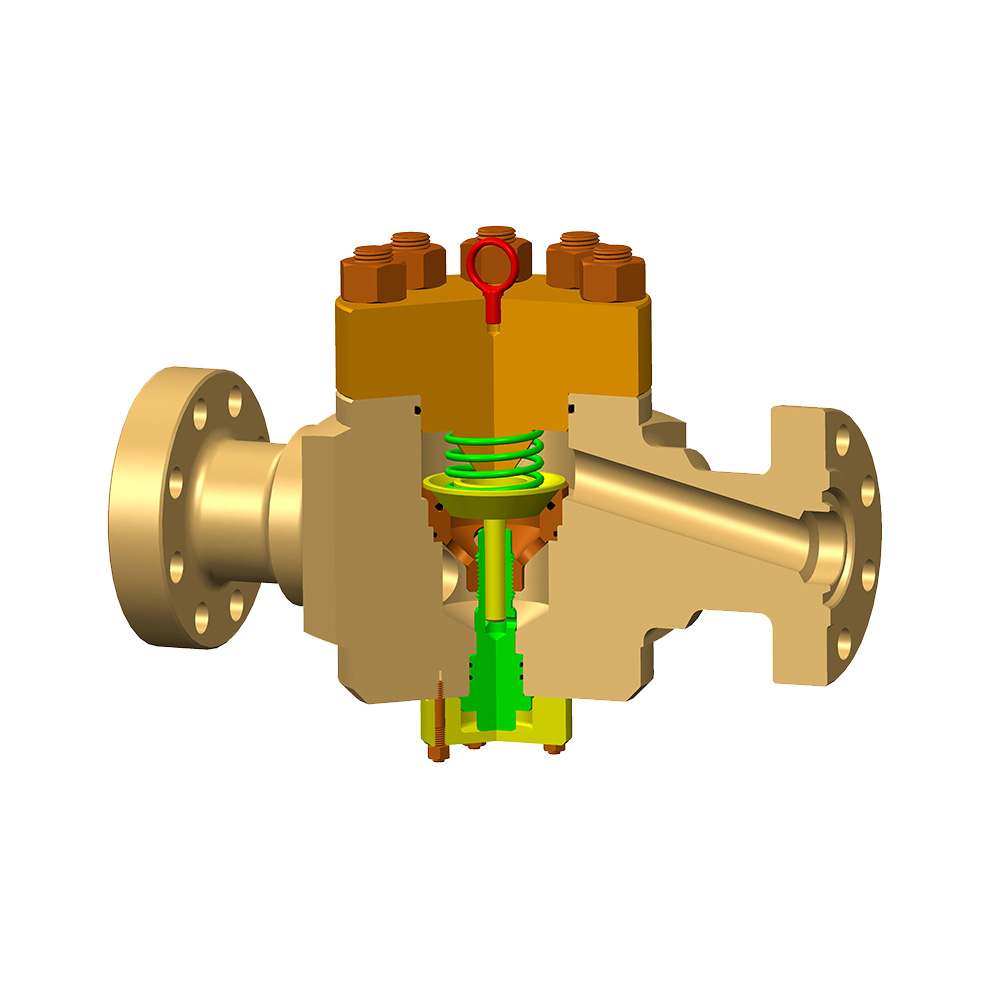
An Expanding Gate Valve is a specialized type of gate valve widely used in oil & gas, petrochemical, pipeline transportation, and other critical industrial systems where tight shutoff, high pressure, and reliability are essential. Unlike conventional gate valves, this valve design uses an expanding mechanism to achieve a superior seal against both upstream and downstream seats.
As global industries demand safer pipelines, reduced leakage, and longer service life, the Expanding Gate Valve continues to gain attention for its unique working principle and proven performance in harsh operating conditions.
- What Is an Expanding Gate Valve?
- How Does an Expanding Gate Valve Work?
- Main Components of an Expanding Gate Valve
- Applications of Expanding Gate Valves
- Expanding Gate Valve vs Other Valve Types
- Advantages of Using an Expanding Gate Valve
- Limitations and Considerations
- Installation and Maintenance Insights
- Future Trends in Expanding Gate Valve Technology
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What makes an Expanding Gate Valve different from a standard gate valve?
- Is an Expanding Gate Valve suitable for high-pressure pipelines?
- Can Expanding Gate Valves be used for bidirectional flow?
- Do Expanding Gate Valves require frequent maintenance?
- Are Expanding Gate Valves suitable for corrosive media?
- Conclusion: Why Expanding Gate Valves Remain a Trusted Choice
What Is an Expanding Gate Valve?
An Expanding Gate Valve is a mechanical isolation valve that uses a two-piece gate system combined with an internal expanding mechanism. When the valve is closed, the gate segments are forced outward against the valve seats, creating a bidirectional, pressure-assisted seal.
This design allows the valve to maintain a tight seal regardless of pressure direction, making it particularly suitable for pipelines that transport oil, gas, steam, or corrosive fluids.
Key Characteristics of an Expanding Gate Valve
- Bidirectional sealing capability
- Zero or near-zero leakage performance
- Minimal seat wear due to controlled expansion
- Suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature systems
- Long service life in demanding environments
How Does an Expanding Gate Valve Work?
The working principle of an Expanding Gate Valve differs significantly from that of a traditional wedge gate valve. Instead of relying solely on downward force, it uses mechanical expansion to create a seal.
Step-by-Step Working Principle
- Valve Opening
When the handwheel or actuator rotates, the stem lifts the gate assembly upward. The two gate segments retract slightly, reducing contact with the seats and allowing smooth flow. - Valve Closing
As the stem moves downward, the gate assembly reaches the closed position. - Gate Expansion
An internal wedge or spring mechanism forces the two gate segments outward. - Sealing Against Seats
The expanded gates press firmly against both valve seats, forming a tight seal on both sides. - Pressure-Assisted Sealing
Line pressure further enhances the sealing force, improving reliability under high pressure.
This controlled expansion ensures consistent sealing without excessive friction or wear during operation.
Main Components of an Expanding Gate Valve
Understanding the internal structure helps explain why the Expanding Gate Valve performs so effectively.
Core Components
- Valve Body – Typically forged or cast steel, designed to withstand high pressure.
- Two-Piece Gate – Expands outward to seal against seats.
- Expanding Mechanism – Wedge, spring, or cam that drives gate expansion.
- Valve Seats – Precision-machined surfaces for tight sealing.
- Stem and Bonnet – Transfer motion from actuator to gate.
- Actuator – Manual, electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic operation.
Applications of Expanding Gate Valves
Thanks to their robust sealing capability, Expanding Gate Valves are widely used in critical isolation applications.
Common Industries
- Oil and gas pipelines
- Refineries and petrochemical plants
- Natural gas transmission systems
- Power generation facilities
- Water injection and high-pressure fluid systems
Typical Use Cases
- Mainline pipeline isolation
- Emergency shutoff systems
- High-pressure block valves
- Media requiring bubble-tight shutoff
Expanding Gate Valve vs Other Valve Types
To better understand the value of an Expanding Gate Valve, it is useful to compare it with other common valve designs.
Expanding Gate Valve vs Wedge Gate Valve
- Sealing Method: Expansion vs wedging force
- Leakage Control: Expanding design offers tighter shutoff
- Seat Wear: Lower in expanding gate valves
- Pressure Direction: Expanding valves seal in both directions
Expanding Gate Valve vs Ball Valve
- Flow Path: Full bore in both designs
- Operating Torque: Lower in expanding gate valves for large diameters
- Maintenance: Expanding gate valves easier to service in-line
- Temperature Resistance: Expanding gate valves perform better at high temperatures
Expanding Gate Valve vs Slab Gate Valve
- Sealing Performance: Expanding gate valves provide mechanical sealing
- Seat Dependency: Slab gates rely more on line pressure
- Leakage Risk: Lower with expanding gate valves
Advantages of Using an Expanding Gate Valve
The growing popularity of the Expanding Gate Valve is driven by several performance advantages.
- Excellent sealing reliability
- Minimal leakage even under fluctuating pressure
- Reduced seat wear and longer valve life
- Suitable for pigging operations
- Low operating torque for large pipeline diameters
- High safety margin for hazardous media
Limitations and Considerations
While the Expanding Gate Valve offers many benefits, certain factors should be considered during selection.
- Higher initial cost compared to simple gate valves
- More complex internal structure
- Requires proper installation alignment
- Not ideal for throttling applications
Installation and Maintenance Insights
Installation Best Practices
- Ensure correct flow direction marking
- Maintain pipeline alignment to avoid stress
- Use appropriate flange gaskets and torque values
- Verify actuator compatibility
Maintenance Recommendations
- Periodic inspection of stem and seals
- Lubrication of moving components
- Seat inspection during scheduled shutdowns
- Replace worn gate components promptly
Future Trends in Expanding Gate Valve Technology
With increasing focus on pipeline safety and emission reduction, manufacturers are investing in improved Expanding Gate Valve designs. Current trends include:
- Advanced seat materials for higher corrosion resistance
- Smart actuators with remote monitoring
- Low-emission stem sealing systems
- Compact designs for space-constrained installations
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What makes an Expanding Gate Valve different from a standard gate valve?
An Expanding Gate Valve uses a mechanical expansion mechanism to seal against both seats, rather than relying solely on wedging force.
Is an Expanding Gate Valve suitable for high-pressure pipelines?
Yes, it is specifically designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Can Expanding Gate Valves be used for bidirectional flow?
Yes, the design provides effective sealing in both flow directions.
Do Expanding Gate Valves require frequent maintenance?
When properly installed and operated, maintenance requirements are relatively low compared to other high-performance valves.
Are Expanding Gate Valves suitable for corrosive media?
With appropriate material selection and coatings, they can handle corrosive fluids effectively.
Conclusion: Why Expanding Gate Valves Remain a Trusted Choice
The Expanding Gate Valve stands out as a reliable and efficient solution for critical isolation applications. Its unique sealing mechanism, durability, and adaptability make it a preferred option for industries where safety, performance, and long-term reliability are non-negotiable.
As infrastructure projects expand and operational standards rise, the role of the Expanding Gate Valve in modern pipeline systems continues to grow, reinforcing its position as a cornerstone of industrial flow control.