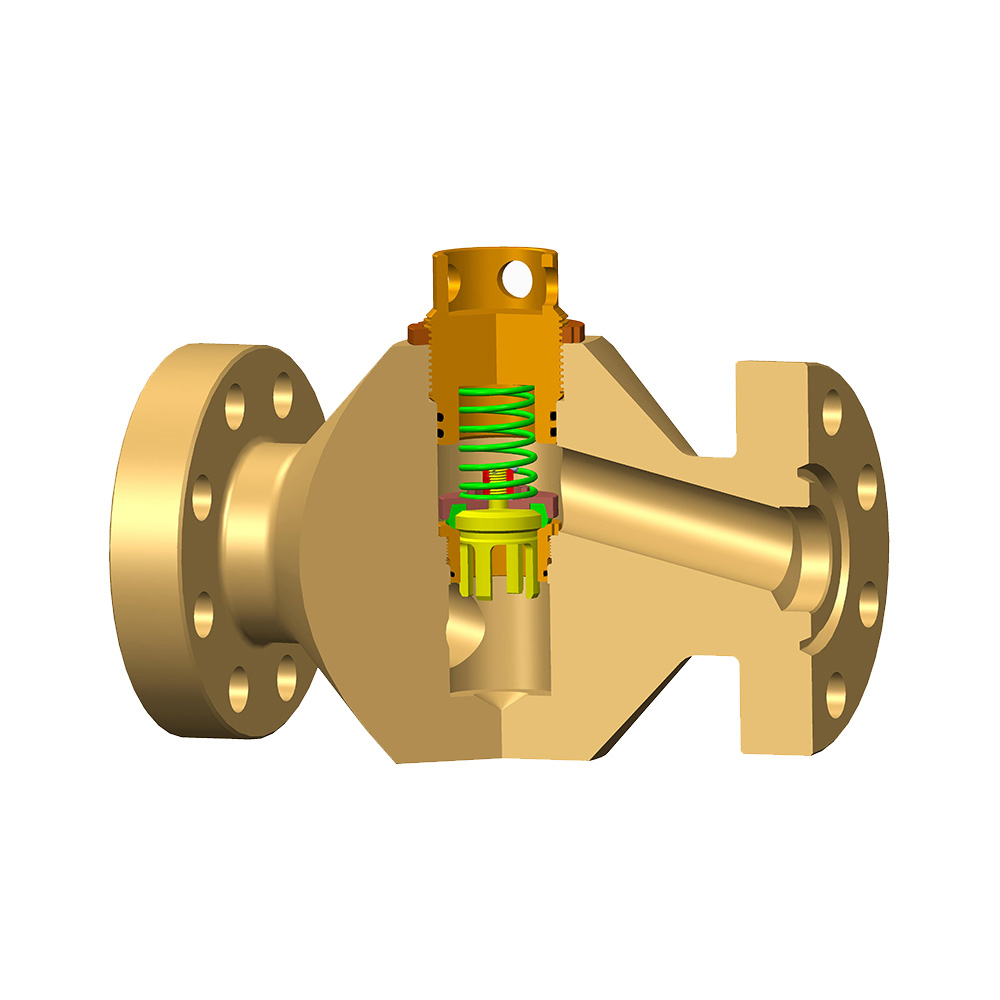
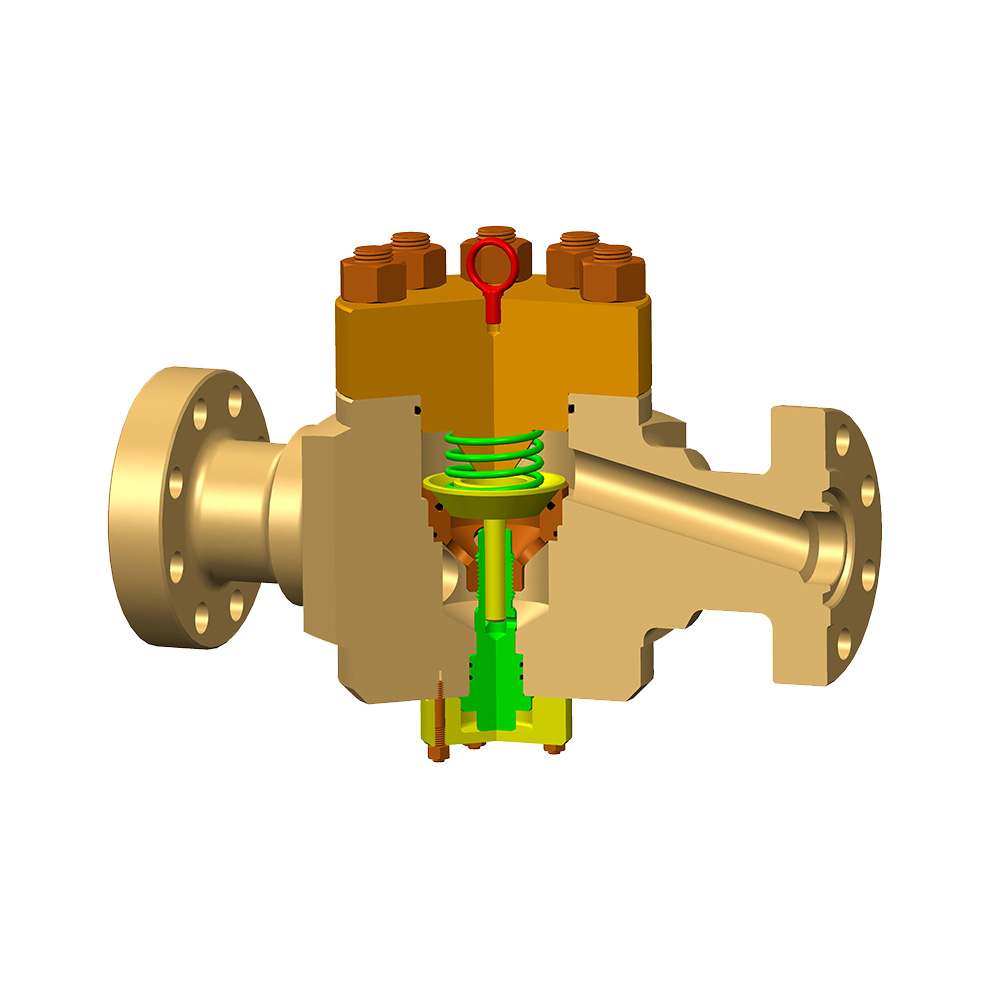
Choke valves are critical components in fluid control systems, designed to regulate flow and pressure in various industrial processes.
Introduction
A choke valve is a type of control valve used to manage fluid flow by creating a pressure drop across an orifice. It is commonly employed in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and water management to maintain system stability and efficiency. This guide explores the mechanics and rationale behind choke valve usage, offering a structured approach to understanding their role in modern engineering.
How Does a Choke Valve Work?
A choke valve operates by restricting the flow of a fluid, typically a liquid or gas, through a constricted passage. This restriction causes a pressure drop, which can be adjusted to control flow rates, prevent surges, or maintain desired pressure levels. The valve consists of a body, an orifice, and an actuating mechanism (such as a stem or sleeve) that modifies the orifice size. In fixed choke valves, the orifice remains constant, while adjustable choke valves allow for real-time modifications. The working principle relies on Bernoulli's equation and fluid dynamics, where reducing the cross-sectional area increases fluid velocity and decreases pressure, enabling precise flow regulation.
Why Is a Choke Valve Needed?
Choke valves are essential for several reasons. They help prevent damage from pressure fluctuations, control production rates in wells, and ensure safe operations in high-pressure environments. For instance, in oil and gas extraction, choke valves manage wellhead pressure to avoid blowouts and optimize resource recovery. Additionally, they are used to reduce erosion in pipelines by controlling fluid velocity and to separate phases in multiphase flows. The need for a choke valve arises from its ability to provide reliable, adjustable control in systems where stability and safety are paramount.
Types of Choke Valves
Choke valves are categorized based on design and functionality. Common types include:
-
Fixed Choke Valves: Feature a permanent orifice size, suitable for consistent flow conditions.
-
Adjustable Choke Valves: Allow operators to change the orifice opening manually or automatically, ideal for dynamic systems.
-
Positive Choke Valves: Use a hardened material to resist erosion in abrasive fluids.
-
Needle Choke Valves: Employ a needle-like component for fine flow adjustments in precision applications.
Each type is selected based on factors such as fluid properties, pressure requirements, and environmental conditions.
Applications
Choke valves are utilized across various industries:
-
Oil and Gas: For well control, production choking, and pipeline pressure management.
-
Chemical Processing: To regulate corrosive or hazardous fluid flows.
-
Water Treatment: In systems requiring flow modulation and pressure reduction.
-
Power Generation: For steam and coolant control in turbines and boilers.
These applications highlight the versatility of choke valves in ensuring operational efficiency and safety.
Comparison with Other Valves
Choke valves differ from other valve types, such as gate valves or ball valves, in their primary function. While gate valves are designed for on/off control and ball valves for isolation, choke valves specialize in flow and pressure regulation. Key comparisons include:
-
Flow Control: Choke valves offer finer adjustment compared to most isolation valves.
-
Pressure Drop: They are optimized for high-pressure drop scenarios, whereas other valves may suffer from cavitation or erosion.
-
Durability: Choke valves often include erosion-resistant features, making them suitable for harsh fluids, unlike standard valves.
This comparison underscores the importance of selecting the appropriate valve type based on system requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the primary purpose of a choke valve?
A choke valve is used to control fluid flow and pressure by creating a restricted passage. -
How do I choose between a fixed and adjustable choke valve?
Fixed choke valves are chosen for stable flow conditions, while adjustable types are preferred for systems requiring frequent changes. -
Can choke valves handle abrasive fluids?
Yes, certain choke valves are designed with erosion-resistant materials to manage abrasive fluids effectively. -
What maintenance is required for choke valves?
Regular inspection for wear, cleaning of orifices, and lubrication of moving parts are common maintenance practices. -
Are choke valves suitable for high-temperature applications?
Choke valves can be engineered for high-temperature use, but material selection and design must align with operational limits.
Choke valves play a vital role in fluid control systems by enabling precise flow and pressure management. Understanding their operation, types, and applications helps in selecting and maintaining these components for optimal performance.