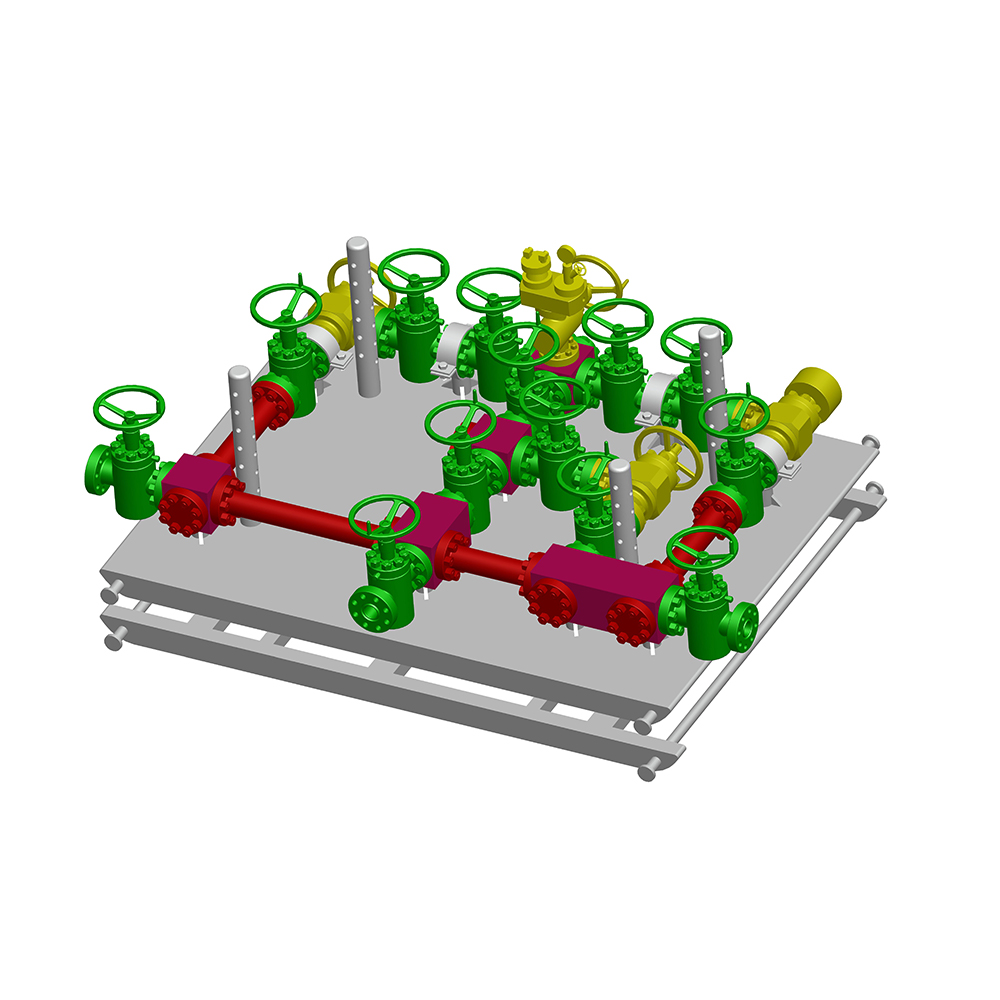
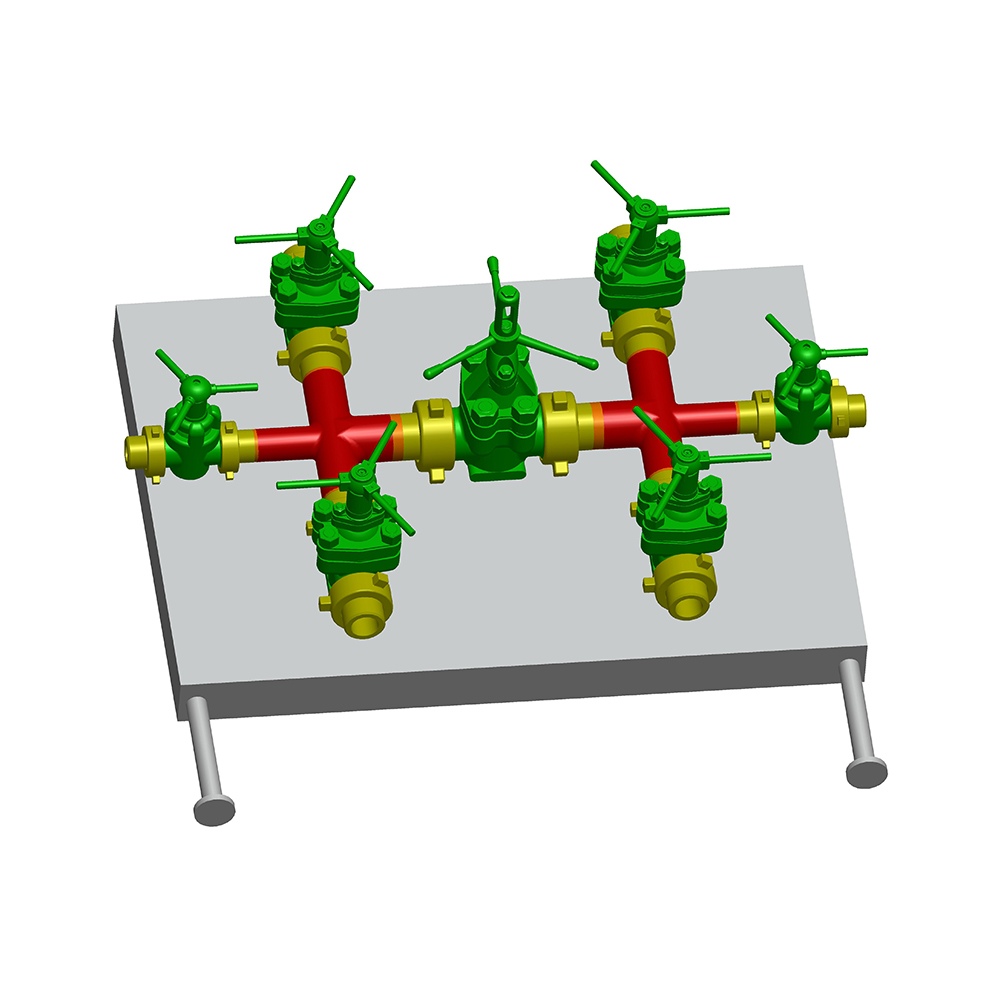
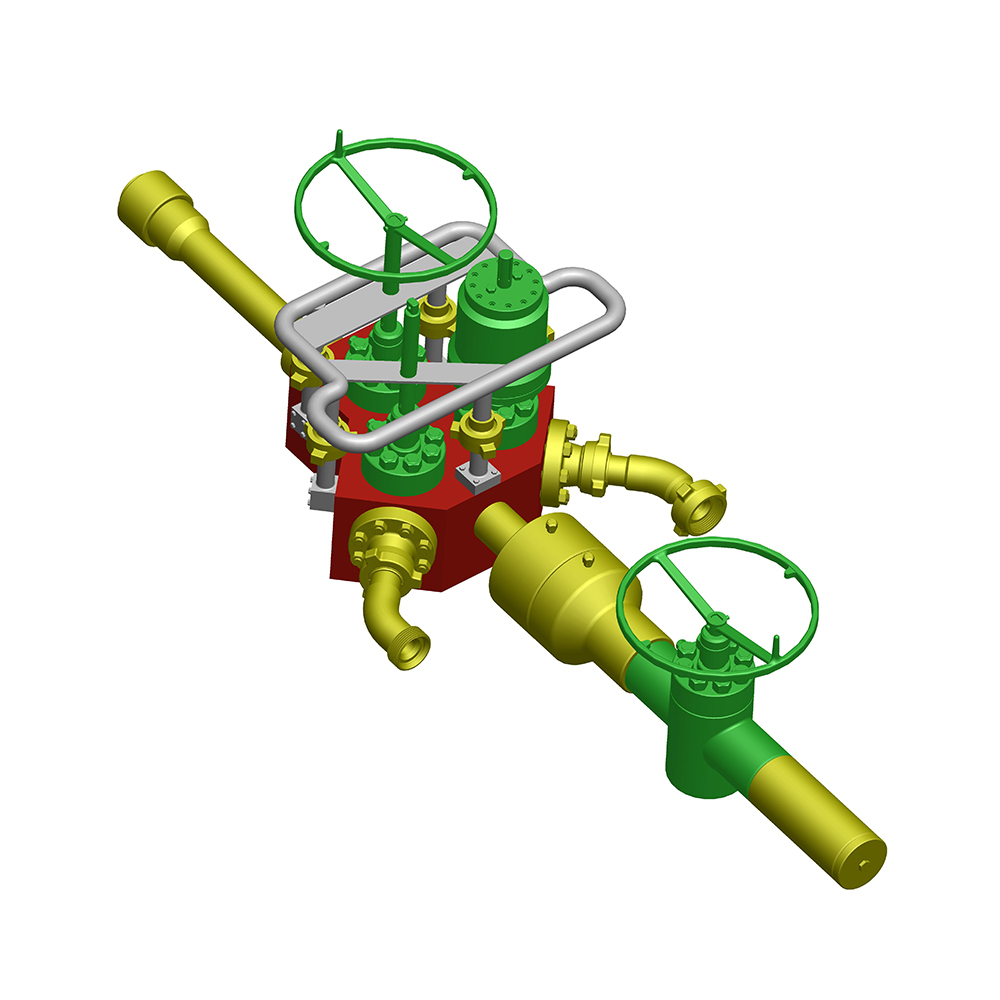
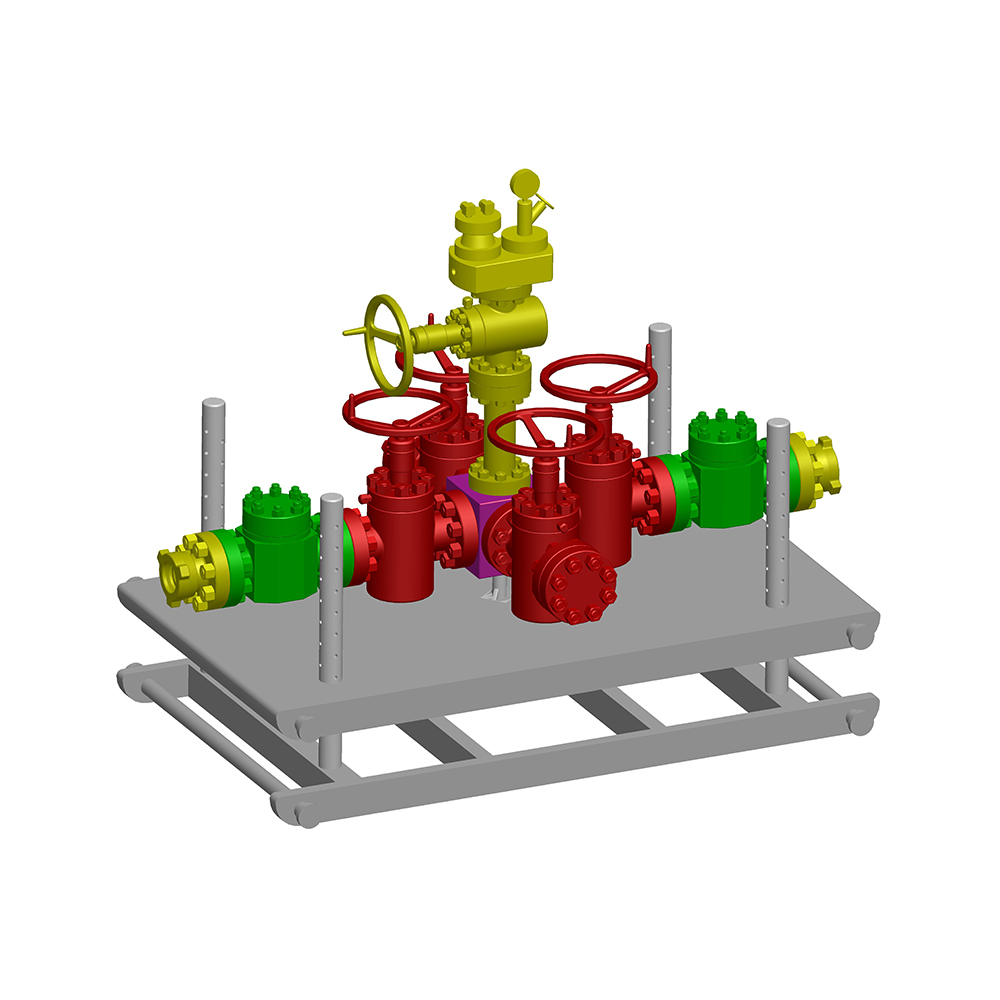
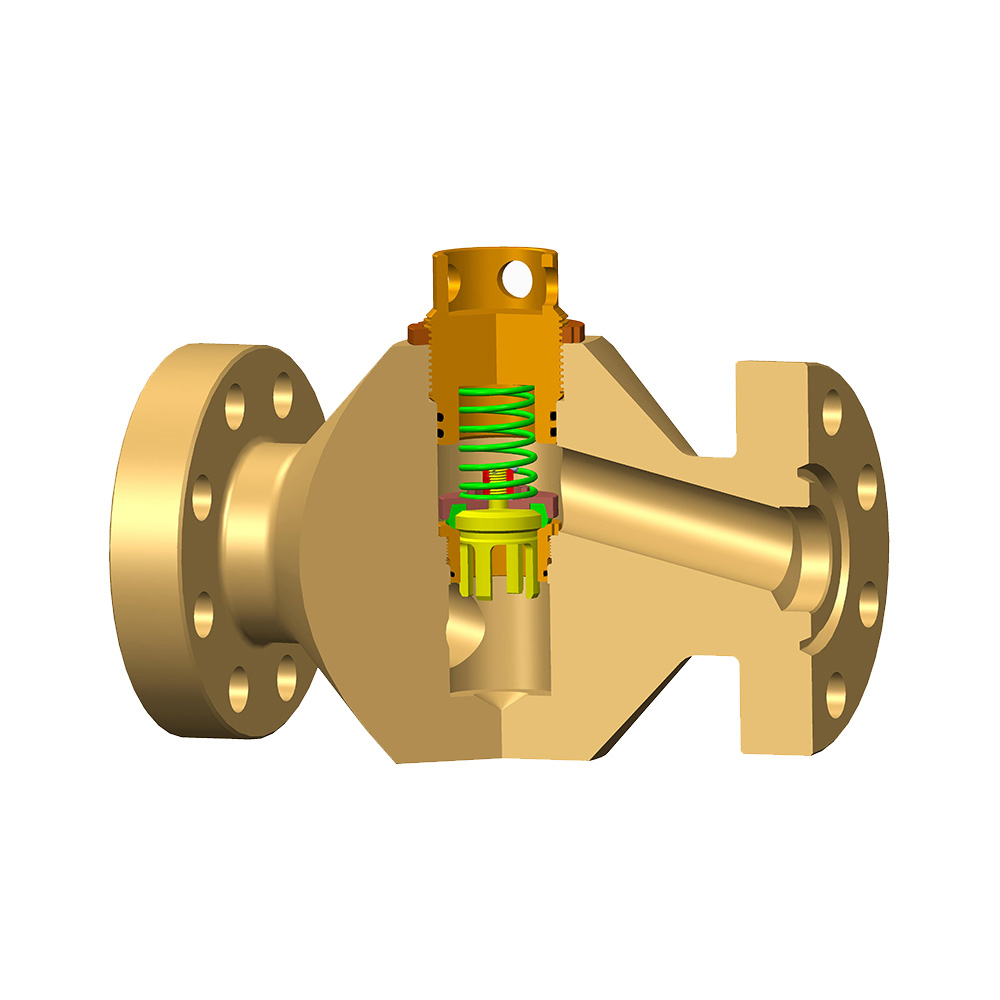
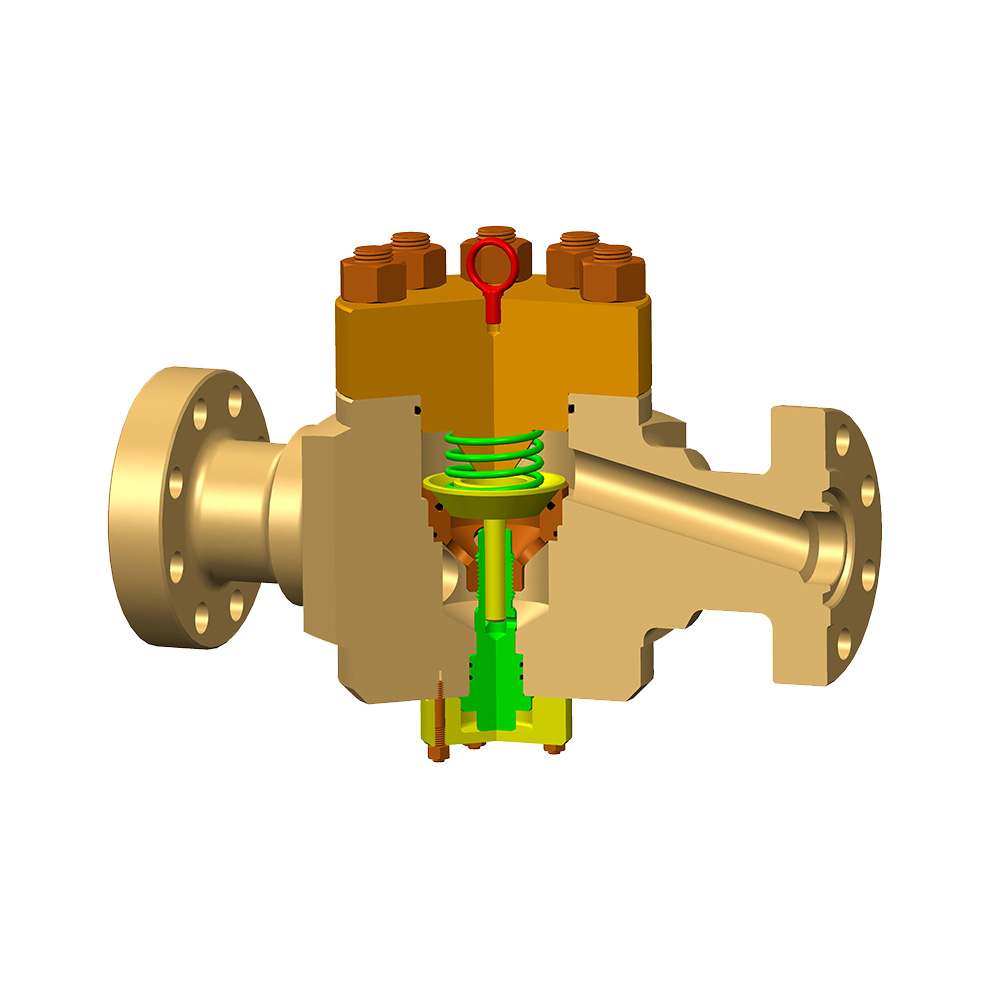
In the oil and gas industry, the choke valve plays a critical role in regulating flow rates and pressures from wells, ensuring safe and efficient operations. Selecting the right choke valve type for specific well conditions is essential to optimize production, prevent equipment damage, and maintain environmental safety.
Concept of a Choke Valve
A choke valve is a device designed to control fluid flow by creating a pressure drop across an orifice. It is commonly used in wellheads to manage the flow of oil, gas, or multiphase fluids from reservoirs to surface facilities. By adjusting the flow area, choke valves help stabilize production, prevent sand erosion, and control well pressure, thereby reducing risks such as blowouts or formation damage.
Types of Choke Valves
Choke valves are categorized based on their design and operation. The main types include:
-
Fixed Choke Valves: These feature a fixed orifice size and are simple in design, suitable for stable well conditions where flow rates do not require frequent adjustment.
-
Adjustable Choke Valves: These allow manual or automated changes to the orifice size, offering flexibility in varying production scenarios.
-
Electric Choke Valves: Operated by electric actuators, these provide precise control and are often used in remote or automated systems.
-
Hydraulic Choke Valves: Powered by hydraulic systems, these are robust and ideal for high-pressure environments, enabling rapid response to changing well conditions.
Each type is engineered to address specific operational needs, such as durability, control accuracy, and compatibility with well fluids.
Applications in Different Well Conditions
The selection of a choke valve depends on factors like pressure, temperature, fluid composition, and well characteristics. For instance:
-
High-Pressure Wells: In such environments, choke valves with reinforced materials and hydraulic or electric actuation are preferred to withstand extreme pressures and ensure reliable performance.
-
Corrosive or Abrasive Conditions: Wells with corrosive fluids or sand require choke valves made from corrosion-resistant alloys or equipped with erosion-resistant components to extend service life.
-
High-Temperature Wells: Choke valves designed with heat-tolerant materials and seals are necessary to maintain functionality under elevated temperatures.
-
Multiphase Flow: For wells producing oil, gas, and water together, adjustable or automated choke valves help manage flow instability and separation issues.
Engineers typically evaluate well data, including flow rates, pressure profiles, and fluid properties, to determine the most suitable choke valve type.
Comparison of Choke Valve Types
A comparative analysis highlights the strengths and limitations of each choke valve type:
-
Fixed Choke Valves are cost-effective and low-maintenance but lack adaptability for dynamic well conditions.
-
Adjustable Choke Valves offer greater control and versatility, though they may require more frequent maintenance.
-
Electric Choke Valves provide high precision and integration with digital systems, but they depend on reliable power sources and can be complex to install.
-
Hydraulic Choke Valves excel in high-pressure applications with fast response times, yet they involve higher initial costs and maintenance for hydraulic components.
This comparison underscores the importance of aligning valve selection with operational requirements, such as control needs, environmental factors, and lifecycle costs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the primary function of a choke valve?
A choke valve controls fluid flow and pressure from a well, aiding in production optimization and safety. -
How do well conditions influence choke valve selection?
Factors like pressure, temperature, fluid corrosiveness, and flow variability dictate the choice of materials, design, and actuation type to ensure durability and efficiency. -
What maintenance practices are recommended for choke valves?
Regular inspection, cleaning, and component replacement are essential, particularly for valves in abrasive or corrosive environments, to prevent failures and extend service life. -
Can choke valves be used in both onshore and offshore applications?
Yes, choke valves are deployed in various settings, but offshore applications often require enhanced materials and automation due to harsh conditions and accessibility challenges. -
Are there standards governing choke valve design and use?
Industry standards, such as those from API (American Petroleum Institute), provide guidelines for design, testing, and operation to ensure safety and performance.
Selecting the appropriate choke valve type is a multifaceted process that demands careful analysis of well conditions and valve capabilities. By understanding the concepts, types, and applications outlined here, industry professionals can enhance operational reliability and safety. Always consult technical specifications and engineering data to support decision-making in choke valve selection.