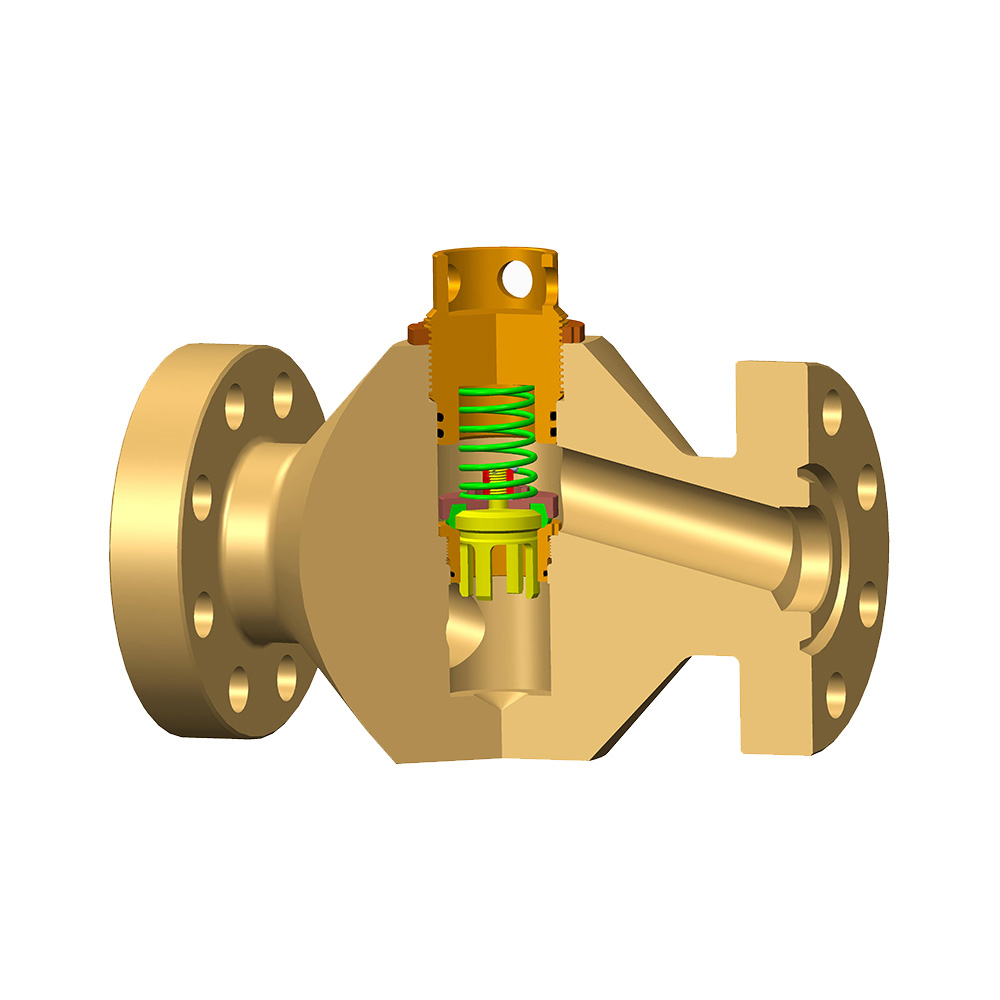
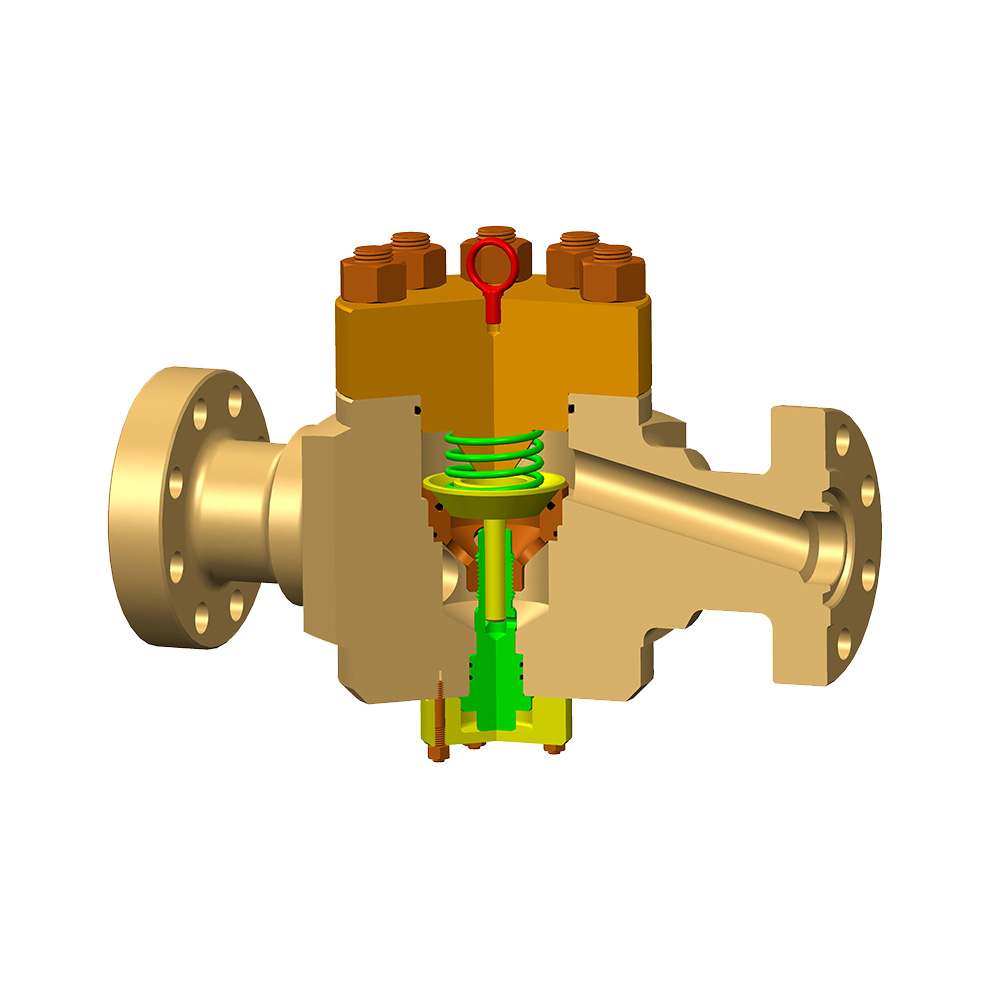
Expanding Gate Valves play a critical role in oil wells by regulating the flow of fluids under high-pressure conditions. As crucial components in controlling wellhead pressure, these valves are subject to considerable wear and tear due to their exposure to harsh operating environments. Maintenance is key to ensuring their longevity and performance. However, maintaining expanding gate valves comes with several challenges that operators must overcome.
- 1. Wear and Tear from Abrasive Fluids
- 2. Corrosion Due to Harsh Environments
- 3. Pressure Fluctuations and Fatigue
- 4. Accumulation of Deposits
- 5. Seal Failures
- 6. Difficulty in Valve Actuation
- 7. Operational Environment and Accessibility
- Comparing Maintenance Needs: Expanding Gate Valves vs. Other Valve Types
- Best Practices for Maintenance
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Wear and Tear from Abrasive Fluids
The constant flow of abrasive fluids in oil wells, such as sand, sediment, and chemicals, can cause significant wear on the components of expanding gate valves. Over time, the valve seats, gates, and seals may erode, affecting the valve's ability to seal properly. This not only leads to inefficient operation but can also result in costly leaks.
2. Corrosion Due to Harsh Environments
Expanding gate valves are often exposed to corrosive substances such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2). These chemicals can rapidly degrade valve components, leading to premature failure. Corrosion is a major challenge in oil well maintenance, and specific coatings or materials must be used to protect the valves from this threat. Operators need to regularly inspect valves for signs of corrosion and replace affected components before they cause more significant damage.
3. Pressure Fluctuations and Fatigue
Pressure fluctuations in oil wells can put expanding gate valves under extreme stress. Over time, this can lead to fatigue and deformation of valve components, resulting in leaks or complete valve failure. Managing pressure spikes and maintaining consistent pressure levels are vital to preventing such issues. Regular monitoring and adjustment of pressure settings can help reduce the risk of fatigue-related problems.
4. Accumulation of Deposits
As the valve operates, debris, wax, and other solid materials can accumulate on the moving parts. This accumulation can prevent the valve from expanding and contracting properly, leading to operational failures. Regular cleaning and maintenance schedules are crucial for removing these deposits to ensure smooth valve function.
5. Seal Failures
The seals within expanding gate valves are essential for maintaining a proper shut-off and preventing fluid leaks. However, seals can degrade over time due to pressure, temperature, and chemical exposure. Seal failures are one of the most common maintenance challenges, often requiring frequent replacements. Monitoring the condition of seals and replacing them at the first sign of wear can prevent more costly failures in the future.
6. Difficulty in Valve Actuation
Another common issue with expanding gate valves is difficulty in actuating the valve, either manually or automatically. This may be caused by internal friction, corrosion, or worn-out actuator components. Proper lubrication, cleaning, and the replacement of actuator parts when needed are essential to keep the valve operating smoothly.
7. Operational Environment and Accessibility
Oil wells are often located in remote or difficult-to-access environments, making regular maintenance of expanding gate valves challenging. The need for specialized equipment, personnel, and safety measures adds complexity to the maintenance process. Operators must plan for logistical challenges and ensure they have the necessary resources available for timely inspections and repairs.
Comparing Maintenance Needs: Expanding Gate Valves vs. Other Valve Types
While expanding gate valves are crucial for oil well operations, it is helpful to compare their maintenance needs with other valve types, such as ball valves or gate valves. The key differences lie in the structural requirements and the specific demands of high-pressure, high-temperature environments in oil wells.
| Maintenance Challenge | Expanding Gate Valve | Ball Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Wear and Tear | Abrasive fluids and erosion are common concerns. | Less susceptible to wear, but still vulnerable to fluid contamination. |
| Corrosion | Higher risk due to prolonged exposure to corrosive substances. | Risk of corrosion is present, but can be mitigated with coatings. |
| Seal Failures | Frequent seal replacements needed due to pressure and chemical exposure. | Seals are generally more durable but still require regular inspection. |
Best Practices for Maintenance
Maintaining expanding gate valves requires a proactive approach that involves regular inspections, timely replacements, and ensuring optimal operational conditions. Operators can adopt the following best practices:
- Regular Inspections: Set up a consistent inspection schedule to detect early signs of wear, corrosion, or seal failures.
- Use of Protective Coatings: Apply corrosion-resistant coatings to prevent degradation from chemicals like H2S and CO2.
- Training and Awareness: Ensure maintenance teams are trained in identifying common issues and troubleshooting valve-related problems.
- Use of Advanced Monitoring Systems: Implement sensors and automated systems to monitor pressure levels, fluid flow, and valve performance in real-time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How often should expanding gate valves be inspected?
Expanding gate valves should be inspected at least once every six months. However, more frequent inspections may be necessary depending on the well’s operating conditions and the severity of the environment.
2. What are the most common signs that a valve needs maintenance?
Common signs include difficulty in actuating the valve, fluid leaks, abnormal pressure fluctuations, and visible wear or corrosion on valve components.
3. Can expanding gate valves be repaired on-site?
In many cases, expanding gate valves can be repaired on-site. However, severe damage may require the valve to be sent to a specialized facility for refurbishment or replacement.
4. What is the typical lifespan of an expanding gate valve?
The lifespan of an expanding gate valve can vary depending on its use and maintenance. Generally, they last between 5 to 10 years before significant repairs or replacements are needed.